The micro and nano enterprises act as vital components that contribute to economic growth and development. Particularly, in a country like India in the age of transitioning from traditional sustenance to a modern industrial economy, micro enterprises act as catalysts towards employment generation, sustainable livelihood, contributing to the country’s GDP and social upliftment of the society. While micro enterprises are defined, nano enterprises are a major, yet formally undefined, segment within the micro enterprise sector. According to organizations working with these nano enterprises at the grassroots level, these businesses earn around Rs. 25,000 per month and work in the informal sector of the economy as kiranas, street vendors, or micro wholesalers. Of the total MSME registrations exceeding 2.1 crores on the Udyam portal as of November 2023, 96.9% were microenterprises. Furthermore, according to the 73rd NSSO survey the number of Unincorporated Non-Agricultural Enterprises (nano enterprises) in India is estimated to be 6.3 crores.
Adhering to the fact that nano enterprises form such a large proportion of the MSME bracket, and yet are unrecognized in the framework, these businesses face various challenges that are exacerbated with the advent of rapid technological developments. Some of the challenges specifically faced by nano enterprises include:
- A lack of distinction between personal and business incomes
- Lack of collateral for loans
- Lack of formal training and skilling
- Substantially minor access to markets for business
The first two contribute to an inability to access formal credit and investments. With the latter two, affecting business growth. Additionally, along with microenterprises, they face issues with compliances, technology adoption, financial discipline, strategic planning, and human resource management. However, for these businesses to survive and grow sustainably they need to be attuned to the demands of the ever-changing digitally-enabled environment. One such comprehensive solution that organizations need to focus on is skilling. According to Ligthelm and Cant (2002), lack of skilled manpower in business operations such as manufacturing, services, and marketing is the main cause of failure for these businesses. India can leverage its vast population to meet this deficit of skilled manpower.
Skilling involves acquiring knowledge to enhance capabilities and gain expertise. According to an Accenture report, skilling is required for organizations to remain competitive in today’s digital world where skills need to be up to date every three to five years compared to being revisited every fifteen to twenty years, a few years back. A World Economic Forum report emphasizes the importance of the same as skill stability- the ratio of key skills required to perform the same job- increases. Skill development offers several advantages to micro and nano enterprises some of which are:
Increase in Productivity
According to an ILO-OECD analysis, employee skills are critical in promoting MSME productivity development at the sector level. Workforce-related skills vary by industry and organized work-based learning programs such as apprenticeships and dual-training programs significantly influence participants’ productivity.
Improved Competencies
Skilling equips employees with the ability to adapt and helps organizations leverage their potential through better operational processes. An impact assessment of enterprise development training programs on entrepreneurial skills among Malaysian microentrepreneurs found that after the program, entrepreneurs were better equipped to recognize market opportunities, manage resources, and build and maintain networking relationships. A survey by the deAsra Foundation reported a willingness by small business owners to learn about social media marketing to grow their businesses.
Innovation
Global MSMEs show an association between innovation and growth, with radical innovation initiatives enhancing market share and sales turnover through diversified goods and services.
The above benefits in turn contribute to business growth and expansion. Basic entrepreneurial training programs have resulted in increased revenues, lower costs, and increased client acquisition that lasts beyond the short term.
India has been running skilling initiatives such as the Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (2015), that provides short-term training of youth through ITIs according to the National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF). Moreover, initiatives such as the establishment of institutes called Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS) throughout the country aim to provide vocational training and skill development. Furthermore, the National Education Policy (2020) recognises the importance of vocational training in education and prioritises it in school curricula.
Yet, such initiatives only meet some of the demand for skilled labor in India. A lack of a formal definition of nano enterprises along with many businesses in the informal sector being unregistered exempts them from government packages and initiatives for MSMEs. There exist major incremental human resource requirements across states.
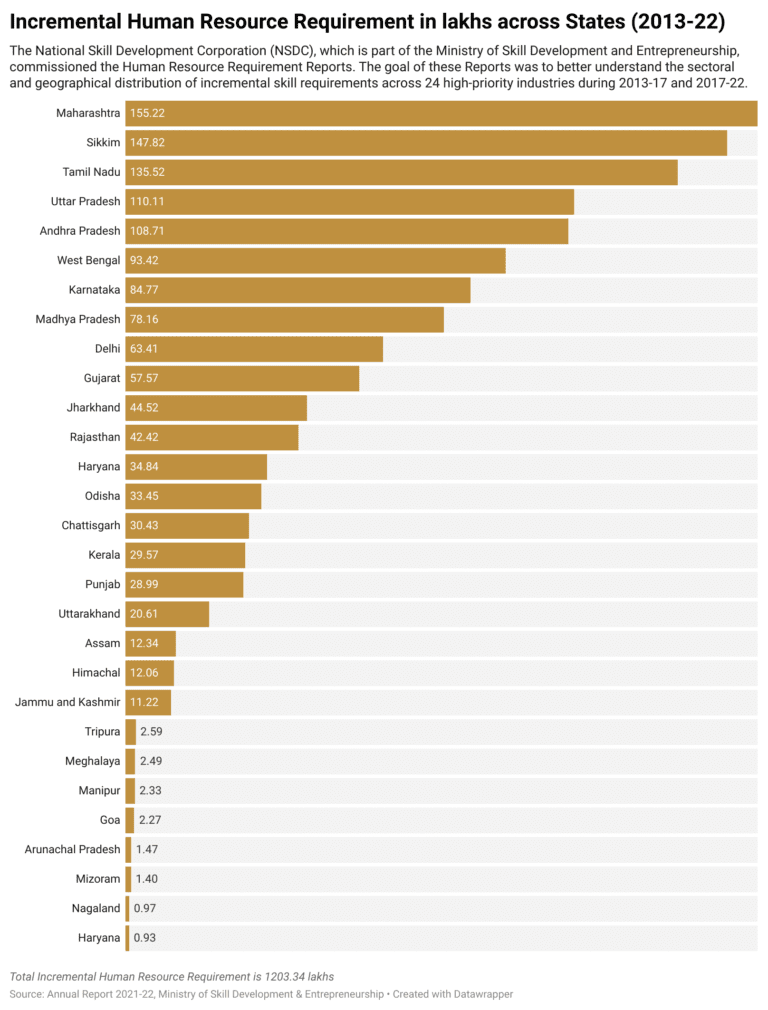
Although advancements in technology create demand for new jobs, their realization is subject to strategic efforts by governments, policymakers, and organizations to invest in developing versatile and adaptive learning strategies ultimately leading to skilling and reskilling. Addressing skill gaps throughout the nano enterprise and microenterprise will facilitate technology adoption and increase workforce resilience. Additionally, capacity building in various aspects of business operations will reduce the rate of failure for these businesses. Addressing the fact repeatedly, nano enterprises being formally undefined their expansion through skilling is a solution for the aforementioned obstacle. Skilling will allow them to address compliance issues, increase technology adoption, and help with access to financial resources through an increase in financial knowledge.
Skilling, therefore, helps fortify the enterprise’s foundations through the ability of its workforce to be versatile and utilize previously unexplored opportunities for their growth. Players in the entrepreneurial ecosystem such as policymakers, government bodies, and skilling institutes should advocate for skilling as an asset for business growth.
We, at CEED through our extensive evidence based policy action research, strive to contribute towards identifying the challenges of nano enterprises and its adjoining areas of skill development with possible solutions and recommendations to empower micro and nano enterprises.
References
Calderon, G., Cunha, J. M., & De Giorgi, G. (2013). Business Literacy and Development: Evidence from a Randomized Controlled Trial in Rural Mexico. https://doi.org/10.3386/w19740
Confederation of Indian Industry & PricewaterhouseCoopers. (2011). Innovation: Changing The MSME Landscape (CII – PwC Research Paper). PricewaterhouseCoopers. https://www.pwc.in/assets/pdfs/publications-2011/innovation-msme-2011.pdf
Dewan, N. (2023, June 28). Why the right skills for MSMEs is necessary to be a future-ready workforce. The Economic Times. https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/small-biz/sme-sector/why-the-right-skills-for-msmes-is-necessary-to-be-a-future-ready-workforce/articleshow/101328438.cms
Mamun, A. A., Muniady, R., Fazal, S. A., & Malarvizhi, C. A. (2019). Micro-enterprise development training and entrepreneurial competencies among low-income households in Malaysia. Asia Pacific Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship, 13(3), 354–366. https://doi.org/10.1108/apjie-06-2019-0042
Michael & Susan Dell Foundation. (2022, April 21). Nano Entrepreneurs in India: Creating Opportunities for Growth. Michael & Susan Dell Foundation. https://www.dell.org/insight/nano-entrepreneurs-india/
The Future of Jobs Report 2018. (2023, May 1). World Economic Forum. https://www.weforum.org/reports/the-future-of-jobs-report-2018/
Udyam Registration | Dashboard. (n.d.). Retrieved November 28, 2023, from https://udyamregistration.gov.in/RealTimeUdyamDashboard.aspx
Workforce Skilling to Lead the Future of Work. (n.d.). Accenture. https://www.accenture.com/us-en/blogs/business-functions-blog/workforce-skilling






